Advanced vs Qualified eSignatures. What’s the difference?
eSignature
- What are digital signatures?
- Key differences between SES, AES and QES
- Advanced Electronic Signature (AES)
- Qualified Electronic Signature (QES)
- What’s new in eIDAS 2024?
- When to use SES, AES, or QES
- Global Recognition of Qualified Electronic Signatures (QES)
- Final Thoughts
As digital transactions continue to reshape global business, the European Union’s eIDAS regulation plays a critical role in standardizing how electronic signatures are defined, validated, and trusted. But what exactly is the difference between an Advanced Electronic Signature (AES) and a Qualified Electronic Signature (QES)? And when should your business use each?
This guide unpacks the legal, technical, and practical differences between SES, AES, and QES, helping you choose the right signature type for every transaction.
#What are digital signatures?
Digital signatures use cryptography to ensure the authenticity, integrity, and non-repudiation of a document. Under EU law, electronic signatures fall into three categories:
Simple Electronic Signature (SES): Typing your name, clicking a checkbox, or uploading a scanned signature. AES offers strong identity assurance without the formalities of QES. It's ideal for contracts where authentication matters but regulatory thresholds are lower.
Advanced Electronic Signature (AES): Secure cryptographic binding to the signer and document
Qualified Electronic Signature (QES): AES + digital certificate issued by a Qualified Trust Service Provider (QTSP)
#Key differences between SES, AES and QES
| Type | Security | Legal Value | Example Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple Electronic Signature (SES) | Low | Weak evidence | Surveys, newsletters, internal consents |
| Advanced Electronic Signature (AES) | Medium | Strong legal weight | HR contracts, banking, enterprise B2B docs |
| Qualified Electronic Signature (QES) | Very High | Equivalent to handwritten signature | Onboarding, notarized agreements, mortgages |
#Advanced Electronic Signature (AES)
- Bound to the signer via asymmetric cryptography (PKI)
- Detects document tampering after signing
- Common for agreements requiring identity assurance
- Used in systems like Signdeer.com, DocuSign and Adobe Acrobat Sign
#Qualified Electronic Signature (QES)
- Issued via a Qualified Trust Service Provider
- Signer identity must be verified (often via video KYC providers)
- Created using a Qualified Signature Creation Device (QSCD)
- Legal presumption of validity across the EU
Ready to deploy AES or QES in your customer journeys?
Signdeer supports both European and global compliance by offering AES and QES layers, fast onboarding with video KYC, and flexible integrations for African and international markets.
Start freeno credit card required. live in minutes.
#What’s new in eIDAS 2024?
- Mandatory integration with the European Digital Identity Wallet (EUDI Wallet)
- Stronger encryption, secure key storage requirements
- Tighter oversight of trust service providers
- Full cross-border QES acceptance across EU states
#When to use SES, AES, or QES
| Use Case | Recommended Type | Compliance Level |
|---|---|---|
| Internal approvals, low-risk emails | SES | Minimal |
| NDAs, employment contracts, KYC | AES | Moderate / eIDAS-compliant |
| Loan agreements, onboarding, notarizations | QES | High / Fully eIDAS-qualified |
#Global Recognition of Qualified Electronic Signatures (QES)
#QES across regions
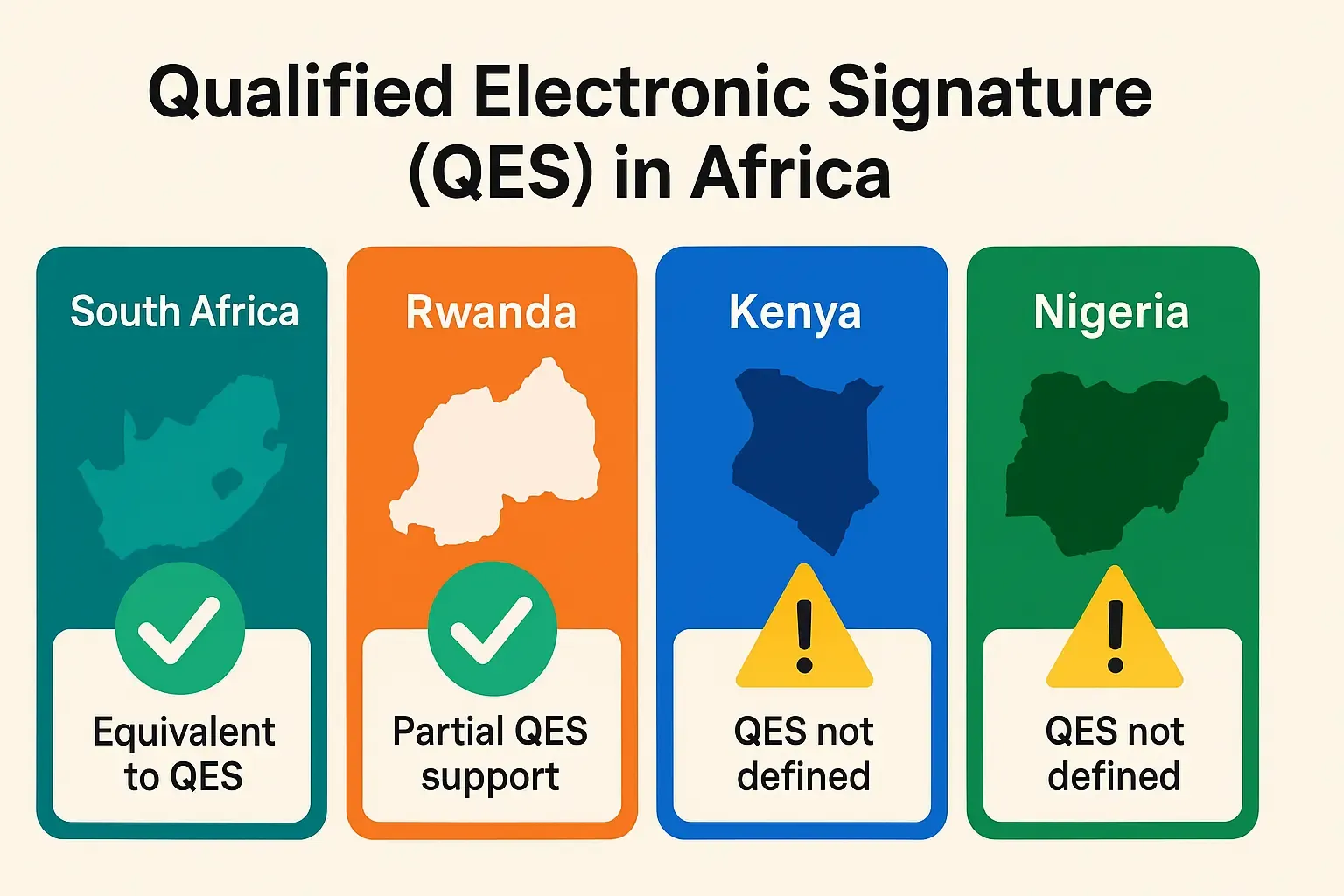
While QES is fully recognized across the European Union under the eIDAS regulation, its acceptance globally varies depending on national laws. Understanding where QES is enforceable can help businesses choose the right strategy for digital contracting.
| Region | QES Recognition | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| European Union (EU) | ✅ Fully recognized | Legally equivalent to handwritten signatures across all EU states under eIDAS. |
| United States | ⚠️ Not automatically recognized | Subject to ESIGN and UETA; QES is not a defined legal category. |
| South Africa | ✅ Partially recognized | The ECT Act defines “advanced” signatures; accredited providers must be used for legal enforceability. |
| Kenya | ⚠️ Recognition evolving | The Kenya Information and Communications Act allows for electronic signatures, but lacks specific QES-level trust framework. |
| Nigeria | ⚠️ Recognition evolving | Recognized under NITDA guidelines; lacks formal trust service infrastructure for QES-level identification. |
| Rwanda | ✅ Legally supported | Law No. 18/2010 recognizes advanced signatures; Rwanda has made significant progress in PKI and national trust services. |
#Strategy for global businesses
For international contracts or onboarding, consider:
- Using QES in EU-facing transactions to meet legal mandates.
- Leveraging AES with strong KYC and timestamping in countries where QES is not defined.
- Including a contract clause that specifies the accepted signature type and jurisdiction to avoid legal uncertainty.
- For African markets, deploy AES with video KYC and audit trails, aligned with evolving e-signature laws in Kenya, Nigeria, and South Africa.
- Use contract clauses specifying jurisdiction and signature type to ensure enforceability across borders.
Solutions like Signdeer’s dual-compliant signing flow support both QES and AES layers, helping African and global businesses scale securely across borders.
#Built for Africa, trusted globally
Signdeer’s platform goes beyond EU borders — supporting businesses across Africa with:
- Localized compliance support in Kenya, Nigeria, Rwanda, and South Africa
- Flexible AES + QES signing flows for hybrid legal environments
- Regional language support and SMS/email-based signer journeys
- Seamless video identity verification
- Integration with the EUDI Wallet (planned)
#Final Thoughts
Choosing between AES and QES isn’t just a legal question, it’s a matter of trust, user experience, and readiness for the digital economy. As global regulations evolve, businesses that adopt flexible, cross-border eSignature tools like Signdeer will remain compliant, trusted, and scalable across Europe, Africa, and beyond.
Ready to implement AES-compliant eSignatures?
Signdeer helps businesses automate onboarding, secure customer agreements, and issue QES remotely while remaining fully compliant, beautifully simple.
Start freeFree consultation. No risk, just real compliance.

Stephen Mungai
Author at Signdeer
Stephen Mungai is part of the team behind Signdeer — a digital signature platform building globally trusted tools from the African continent outwards.
View full profile →